
What is Composting ?
Composting is a process of biological decomposition of organic constituents of wastes under controlled conditions to a state sufficiently stable for nuisance free storage and utilization. There are mainly 2 Methods of composting in India which is explained below.
Composting can also be defined as the process of transformation of organic materials through decomposition into a soil like material called compost.
There are two types of micro-organisms invovled in composting.
Aerobic – Which decompose organic materials in presence of oxygen.
Anaerobic- Which decompose organic matter in absence of oxygen.
Methods of Composting
There are mainly 2 Methods of composting in India.
1. Bangalore Method of Composting
2. Indore Method of Composting
Bangalore Method of composting
The Bangalore method of composting is an anaerobic method carried out in out in pit, In this method the composting material is not mixed and is allowed to remain in the pit for about 4 to 6 months.
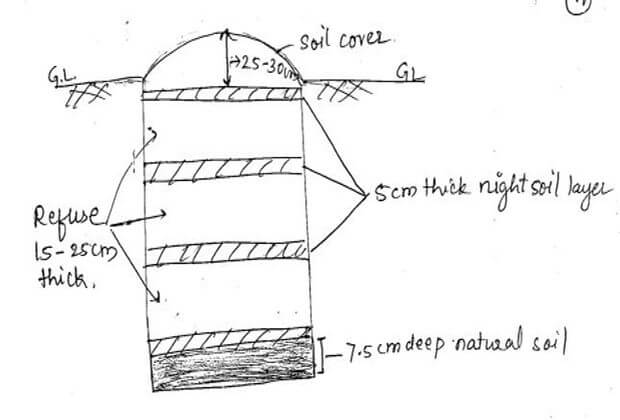
Method:
1. About 150cm trench is to be developed and night soil layer of about 5cm thick is spread in this trench. Normally night soil flows rapidly by itself.
2. Succeeding layers of solid waste and night soil are added in a similar manner with pit stack of about 30cm above ground or pit curb.
3. Each layer of night soil is immediately covered with waste and top most layer of waste should be at least 20cm thick.
4. The composting mass develops a temperature of about 600C in a few days.
5. After the material has been decomposed for a several days, the volume decreases and the piles settles to 1/2 to 2/3 of original depth.
6. New layer of night soil and water can be added to the pit until the level is again above the pit curb.
7. The pile may be covered with 5cm layer of earth to help prevent the escape of ammonia.
8. Pit is completely filled and a final soil layer is laid to prevent fly breeding, entry of rain water into pit and for conservation of released energy.
9. Marerial is allowed to decompose for 4-6 months after which a stabilizes material is taken out and used as a compost.
It can be removed and directly put on soil or screened
Also Read – Wastewater Treatment Process | Why it is Important?
Indore Method of composting
Indore method is an aerobic method of composting and it is most suitable for Indian climate.
1. This process of composting is similar to that of Bangalore process. i.e. filling of alternate layers of similar thickness in pit.
2. To ensure aerobic conditions materials is turned at specific intervals for which a 60cm strip on longitudinal side of the pit is kept vacant.
3. It also keeps maintaining high temperature ,more rapid & uniform decomposition and more effective fly control.
4. For starting turning operation, 1st turn is manually given using long handled rakes 4 to 7 days after filling.
Turning performs 3 functions
- It completes the mixing of refuse & night soil.
- The materials at top nd sides which are not subjected to high temp are also subjected to high temp.
- The materials are aerated, which is an essential feature of aerobic stabilization.
5. 2nd turn is given after 5-10 more days.
6. Further, turning is not required and compost is ready in 2 to 4 weeks.
Also Read – Activated Sludge Process -Types| Components |Advantages |Description
