Remote sensing
Remote sensing is defined as “The art, science, and technology of obtaining reliable information about physical objects and the environment, through the process of recording, measuring and interpreting imagery and digital representations of energy patterns derived from non-contact sensor systems”.
According to India’s National Remote Sensing Agency- “Remote Sensing is the technique of acquiring information about objects on the earth’s surface without physically coming into contact with them”.
Principles of remote sensing
- Detection and discrimination of objects or surface features means detecting and recording of radiant energy reflected or emitted by objects or surface.
- Different objects return different amount of energy in different bands of the electromagnetic spectrum, incident upon it.
- Depend upon the property of material (physical, structural, and chemical), surface roughness, angle of incidence, intensity, and wavelength of radiant energy.
Components of remote sensing
These are the components involved in remote sensing process
- Energy Source or Illumination (A)
- Radiation and the Atmosphere (B)
- Interaction with the Target (C)
- Recording of Energy by the Sensor (D)
- Transmission, Reception, and Processing (E)
- Interpretation and Analysis (F)
- Application (G)
1 Energy Source or Illumination (A)
The first requirement for remote sensing is to have an energy source of electromagnetic radiation to illuminate the target. Sensors can use either external Energy source(Sun) or have their own energy source of illumination.
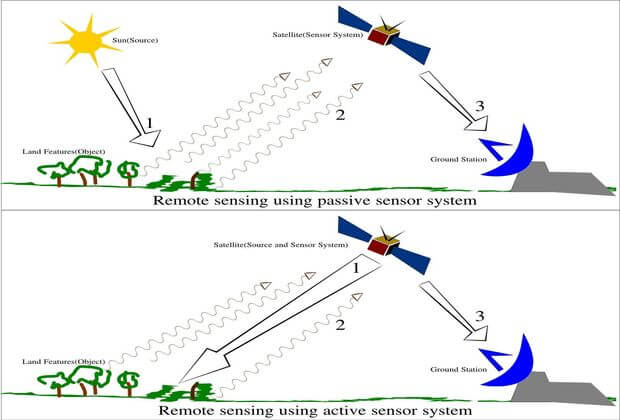
- Sensors using external source of energy are called Passive remote sensor.
- Sensors Sensors using their own energy source called Active remote sensor.
2 Energy Interactions with Atmosphere (B)
The energy travels from the source to the target, It passes through the earth’s atmosphere which contains obstacles such as haze, clouds, smog etc.
3 Interaction with the Target (C)
The electromagnetic Radiation that is not absorbed or scattered in the atmosphere can reach and interact with the Earth’s surface.
4 Recording of Energy by the Sensor (D)
When the energy has been scattered by, or emitted from the target, It is collected through a sensor (remote – not in contact with the target) and record the electromagnetic radiation.
5 Transmission, Reception, and Processing(E)
The energy recorded by the sensor has to be transmitted, often in electronic form, to a receiving and processing station where the data are processed into an image (hardcopy and/or digital).
6 Interpretation and Analysis (F)
The processed image is interpreted and analyzed, visually or digitally or electronically, to extract information about the target which was illuminated.
7 Application (G)
- Geology: it is used for geological mapping;
- Hydrology: Used in monitoring wetlands and snow cover;
- Agriculture: Helps in identification of type of crop , crop condition monitoring, soil moisture measurement, and soil tillage and crop residue identification.
- Forestry: Useful clear-cuts and linear features mapping, biomass estimation, species identification and fire scar mapping;
- Oceanography: sea ice identification, coastal wind field measurement, and wave slope measurement.
- Shipping: for ship detection and classification. Coastal Zone: for shoreline detection, substrate mapping, slick detection and general vegetation mapping.
- Military/Security Applications: Helps in detecting or locating metal objects.
Related – Best Civil Engineering Software Updated List 2021
Limitations of Remote Sensing
- Its utility is often oversold.
- It is not a solution that will provide all the information needed for conducting physical, biological, or a science.
- It simply provides some spatial, spectral, and temporal information.
Also Read – Methods for determining the bearing capacity of soil
