What are rocks?
Rocks are naturally occurring solid substances which are made of one or more minerals or organic matters.
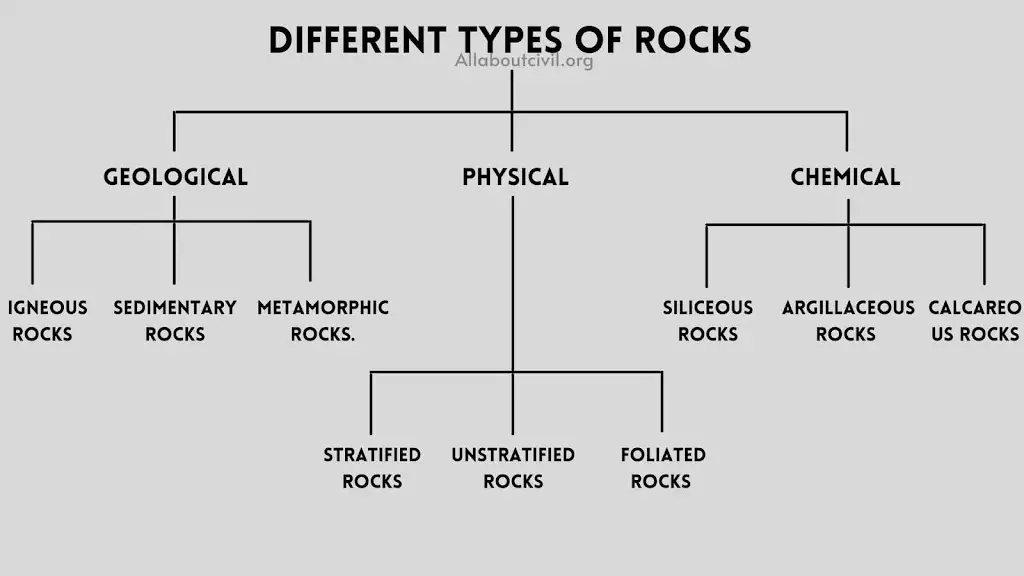
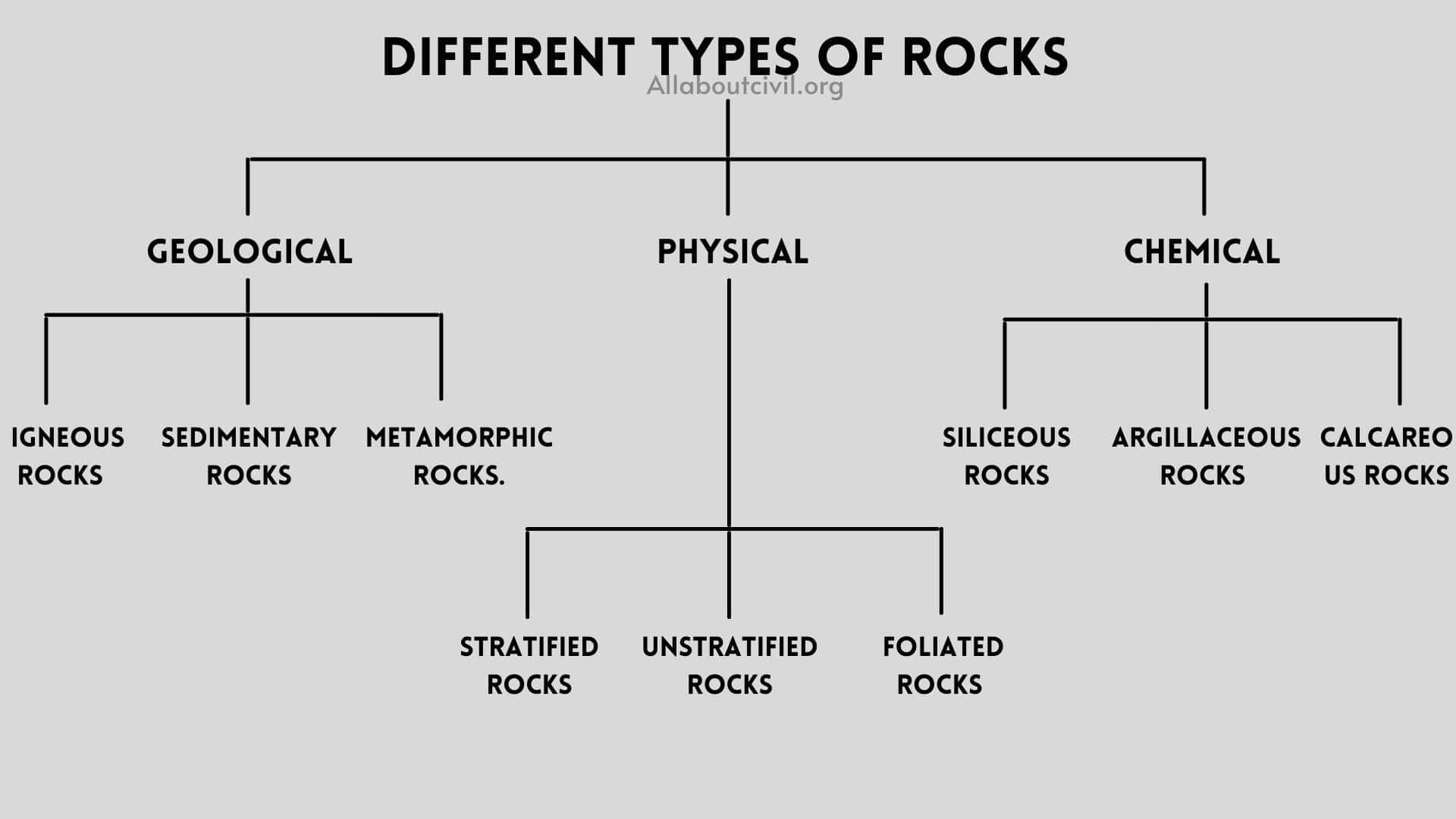
Different Types of Rocks
Rocks are majorly classified into 3 types
1. Geological
2. Physical
3. Chemical
1. Geological Classification
Based on their origin or geological formation rocks are classified into 3 types
a. Igneous Rocks
b. Sedimentary Rocks
c. Metamorphic Rocks.
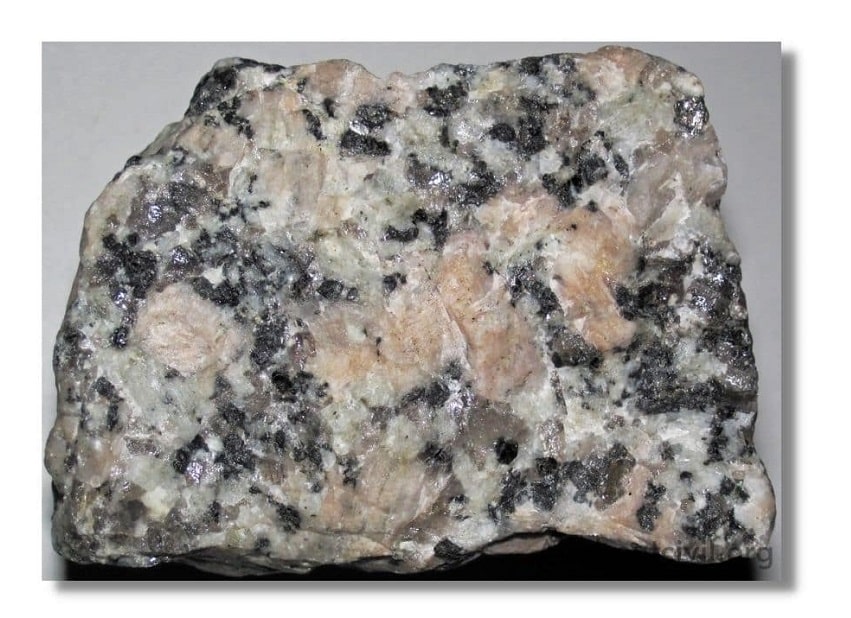
a. Igneous Rocks:
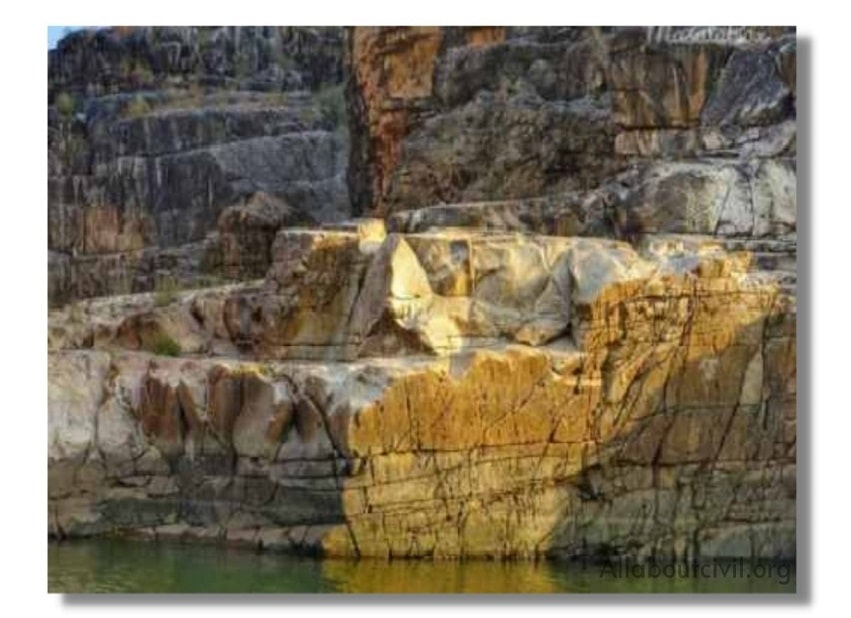
Igneous rocks are formed by cooling and solidifying of magma below the earth surface. Generally igneous rocks are strong and durable.
Examples-Granite, trap and basalt
Hypabyssal Rock- When lava or magma hardens at shallow depth from the earth surface results in formation of finely grained crystalline surface. Example-Granite
Volcanic Rocks- When cooling of lava takes place at the top surface of earth results into non-crystalline and glassy texture. Example-Trap and basalt
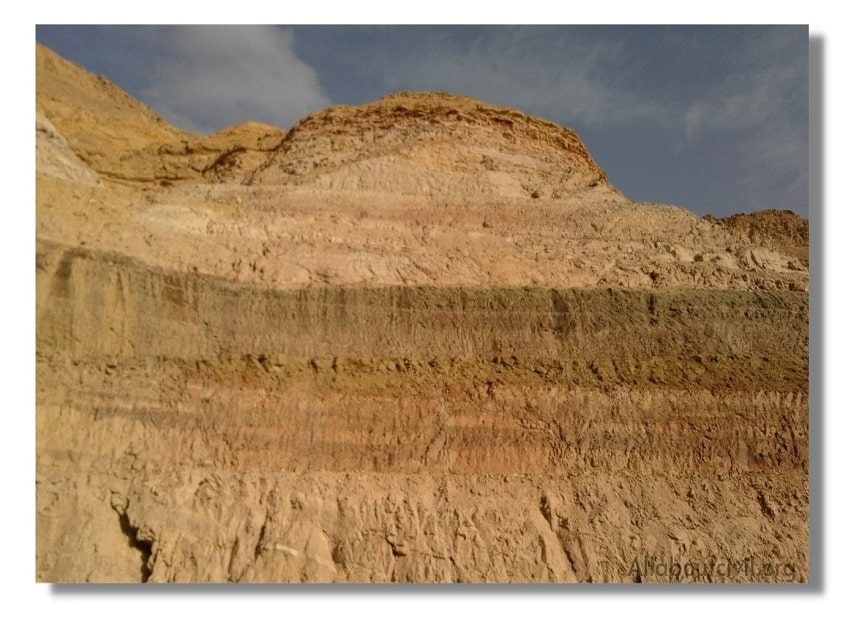
b. Sedimentary Rocks:
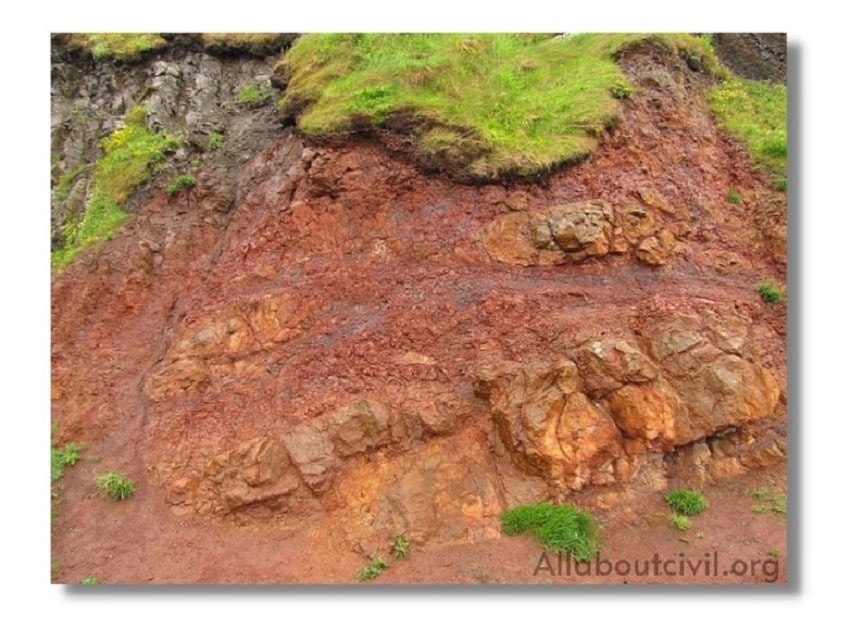
Sedimentary rocks are formed by deposition of sediments obtained by weathering action of water, wind and frost of pre-existing rocks. The disintegrated material is carried by wind and water.
Flowing water deposits its suspended materials at some points of obstacles to its flow. These deposited layers of materials get consolidated under pressure and by heat. Chemical agents also contribute to the cementing of the deposits.
The rocks thus formed are more uniform, fine grained and compact in their nature.
Examples-Sand stones, lime stones, mud stones etc.
c. Metamorphic Rocks:
Due to metamorphic action of pressure and internal heat Previously formed igneous and sedimentary rocks under go changes resulting in formation of metamorphic rocks.
Example-Due to metamorphic action granite becomes gneiss, trap and basalt change to schist and laterite, lime stone changes to marble, sand stone becomes quartzite and mud stone becomes slate.
Related-Different types of landscaping rocks and stones
2. Physical Classification
Based on the physical structure, the rocks may be classified into 3 types as follows:
a. Stratified rocks
b. Unstratified rocks
c. Foliated Rocks
a. Stratified Rocks:
Stratified rocks are having a layered structure. These are separated by planes of cleavage or stratification. These can be easily split up along the planes.
Examples-Sand stones, lime stones, slate etc.
b. Unstratified Rocks:
These rocks are just opposite of stratified. They posses same kind of structure throughout their body. Unstratified Rocks are crystalline and compact grains. They cannot be split in to thin slab.
Examples-Granite, trap, marble etc.
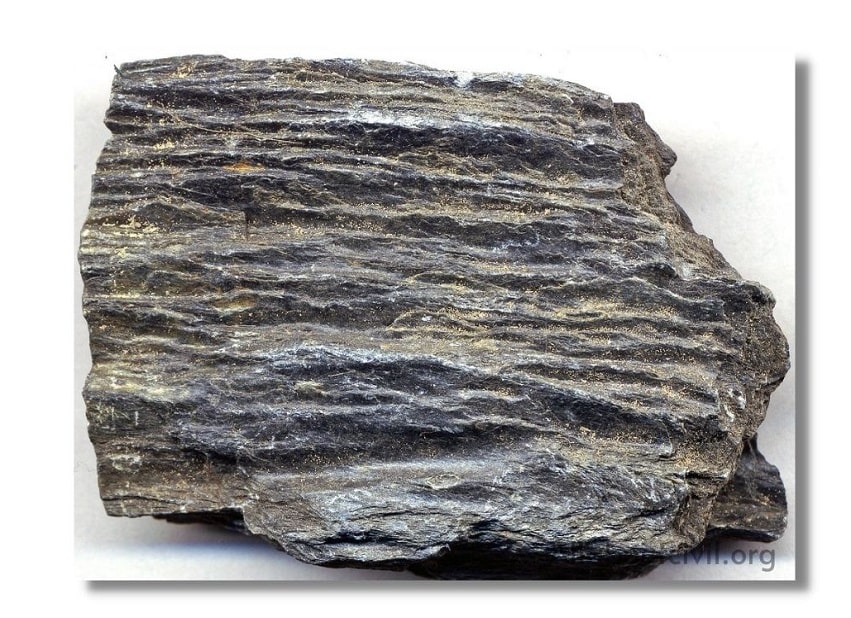
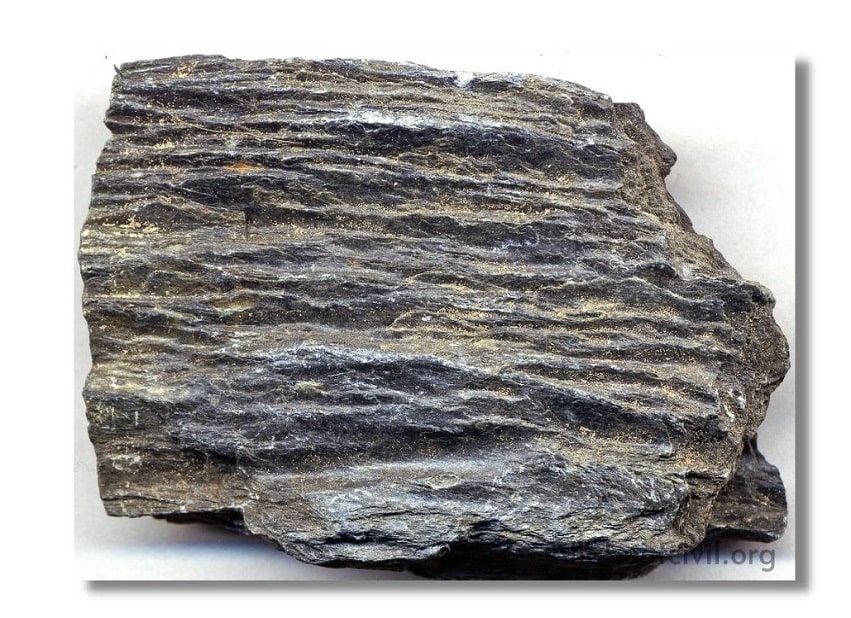
c. Foliated Rocks:
Foliated rocks have a tendency to split along a definite direction only. The direction need not be parallel to each other as in case of stratified rocks. This type of structure is very common in case of metamorphic rocks.
Examples-Gneiss, Schist, slate
3. Chemical Classification
On the basis of their chemical composition these are classified into 3 types as follows:
• Siliceous rocks
• Argillaceous rocks
• Calcareous rocks
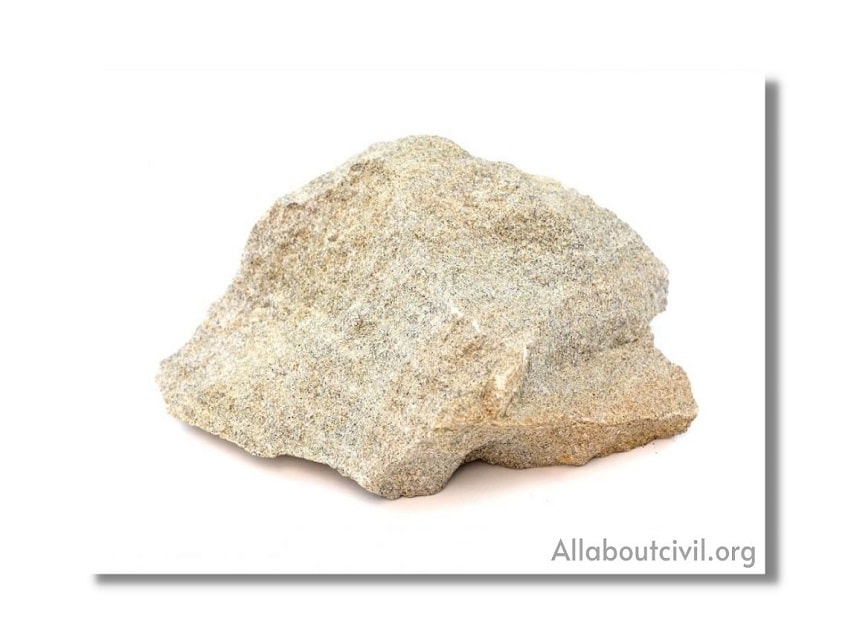
a. Siliceous rocks:
These are called siliceous rocks because main content of these rocks is silica. Due to presence of large amount of silica these are hard and durable.
Examples-granite, trap, sand stones etc.
b. Argillaceous rocks:
In this type of rocks the main constituent is argil i.e., clay. Hence they are called argillaceous rocks. These rocks may be dense and compact or soft. They cannot withstand shock and can be crushed easily because of their brittleness.
Examples- Slates and laterites
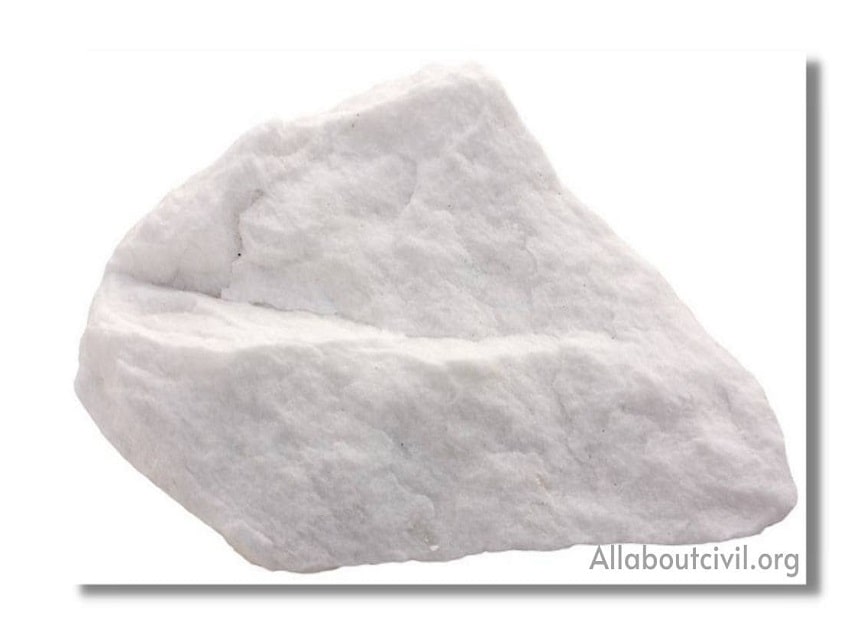
c. Calcareous rocks:
Calcareous rocks contains predominant amount of calcium carbonate. These are generally hard but durability depends on surrounding constituents. Limestone is a calcareous rock with sedimentary origin while marble is a calcareous rock with metamorphic origin.
Examples- Limestone, Dolomite and Marble etc.
Also read: What are the Causes of Failure of Earthen Dam