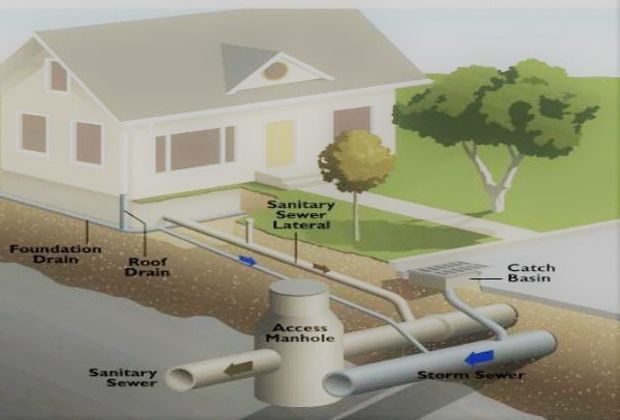
House Drainage System
House drainage system is an arrangement provided in a house or building, in order to collect and convey the wastewater through drain pipes, by gravity, to join either a public sewer or a domestic septic tank.
House Drainage System is a collective system of important components like W.C, Bathrooms, Sinks, Wash basins, etc. When residents of the house or building make use of these components resulting in the formation of waste water and wastewater from W.C, bathrooms, sinks and washbasins should be properly disposed into municipal sewers.
It is therefore necessary to construct a system of conveyance of wastewater from W.C, bathrooms, kitchens and washbasins and disposal to the municipal sewer. This system is known as house drainage system.
Also Read – What is Sewerage? Different Types of Sewage system
Purpose of House Drainage System
The main purpose of house drainage system is to convey the wastewater, But here are some other important purpose of house drainage system are as following
- Drainage system helps to maintain healthy conditions in the building
- It dispose off wastewater as quickly as possible
- It prevents the entry of foul gases from the sewer
- Waste from wash basins, sinks, etc are Collected and removed systematically
Principles of Drainage system for house
The following principles must be followed for the efficient House Drainage system :
- The lavatory blocks(sink,wash basins,toilet etc) should be so located that the length of drainage line is minimum.
- Drainage pipe must be laid by the side of the building or house rather than below the building or house.
- All the drains should be aligned straight between successive inspection chambers. Therefore, sharp bends and junctions should be avoided through chambers.
- The slope of the drains must be sufficient to develop self cleansing velocity and convey the waste to the sewage by gravity.
- All the drainage connections must be water tight.
- Drainage system must contain enough number of traps at suitable locations.
- The size of drain should be sufficient, so that flooding of the drain doesn’t take place while handling the maximum discharge.
- Rain water pipes should drain out rain water directly into the street gutters from where it is carried to the storm water drain.
- All the materials and fittings of drainage system should be hard, strong, resistant to corrosive action.
- Formation of air locks, siphon-age, under deposits etc. should be minimized.
Drainage Fittings
These are some of underground drainage fittings are provided to collect wastewater from washbasin,toilet and sink etc and convey to sewage.
- Pipes
- Traps
Pipes
In a house drainage system, Pipe is main material which have the following designations, depending upon the function it carries :
- Soil Pipe – Soil pipe is a underground drainage pipe through which human excreta flows. Most commonly used sizeof soil pipe is 100mm.
- Waste Pipe – It is a pipe which carries only the liquid waste, usually seen below sink and washbasins and it doesn’t carry human excreta.Most commonly used size of waste pipe is 30 to 75 mm.
- Vent Pipe – It is a pipe which is provided for the purpose of ventilation of the system. A vent pipe is open at top and bottom, to facilitate exit of foul gases. It is 1 m higher than the roof level.Most commonly used size of vent pipe is 50 mm.
- Rain water Pipe – This pipe carries only the rain water. Most commonly used size of rain water pipe is 75 mm.
- Anti-siphonage Pipe – It is a pipe which is installed in the house drainage to preserve the water seal of traps. Most commonly used size of anti-siphonage pipe is 40-50 mm.
Traps
Traps are bent fittings which retains some water, maintaining a water seal in order to prevent passage of foul gases. Traps are classified into two types based on their shape and uses.
Based on Shape
- Q-Trap
- P-Trap
- S-Trap
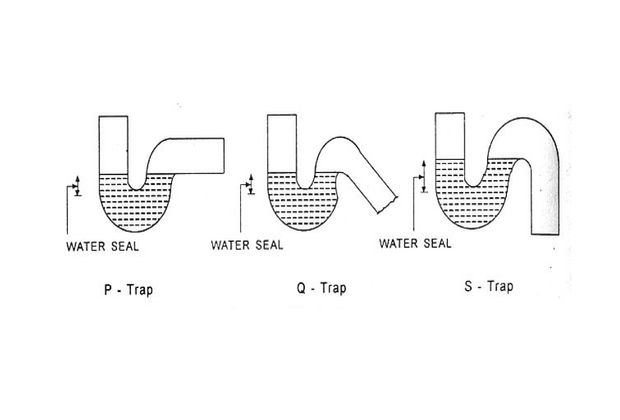
Based on uses
- Gully Trap
- Nani Trap
- Intercepting Trap
Gully Trap
A Gully trap or gully is provided at a junction of a roof drain and other drain coming from kitchen or bathroom. The foul sullage can enter through the side inlet which is also known as back inlet and unfoul rain water enter from the top which is covered with cast iron grating or jallis.
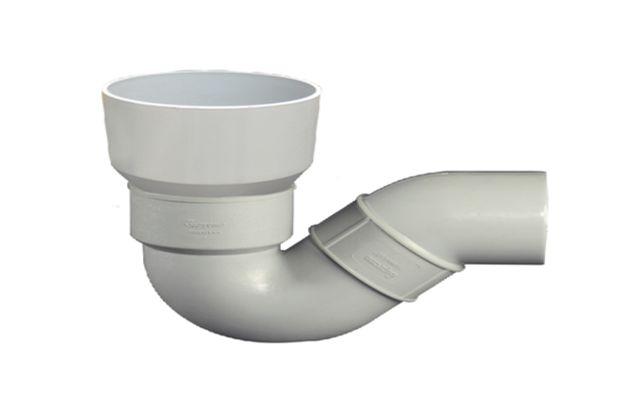

Gully traps may either have a P shaped or Q shaped water sealing arrangement. The water seal is normally 50 mm to 75 mm deep.
Floor Trap or Nani Trap
Nani traps are provided to collect waste water or sullage from floors of the rooms like bathroom, toilet, wash area etc.
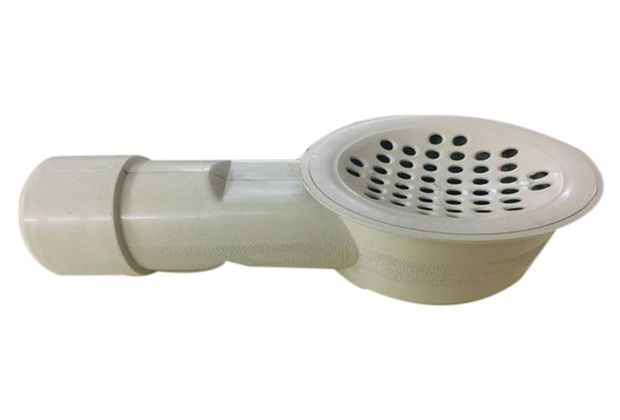

These traps are provided with stainless steel or galvanised gratings which are commonly known as Jallis at the top that prevents entry of solid matters and reduces blockage chances. Those jallis can be removed for frequent cleaning of traps.
Intercepting Trap
Intercepting trap are provided at the junction of house drain connecting with public sewer. It has deep water seal of 100 mm, so prevents the entry of foul gases from public sewer line into the house drains.
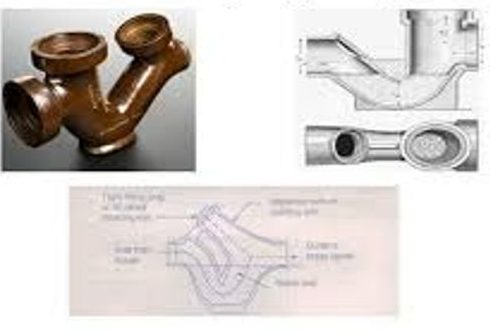
It has opening at the top for frequent cleaning, termed as cleaning eye / rodding arm.
Sanitary Fittings
Sanitary fittings are commonly used in house or buildings for collection and removal of waste water or foul matters.
Sink
These are generally used in kitchen for cleaning purpose of utensils.

Wash Basin
Wash basins usually made up of pottery or porcelain ware. It is oval in shape as bowl, with an overflow slot at the top.

Wash basins are commonly used in bathroom and can be used where face wash and hand wash are necessary.
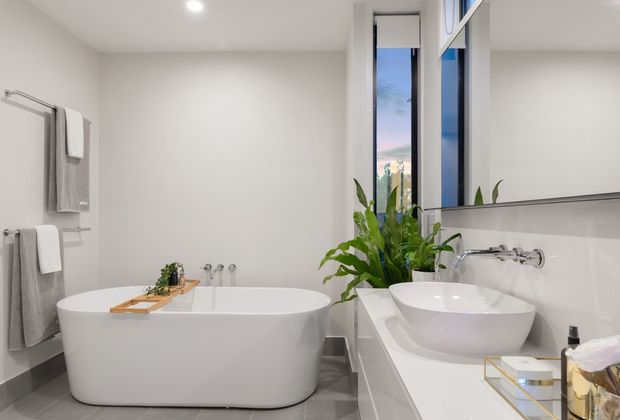
Bath Tub
Many bathtubs are usually made of ceramic or porcelain and enough space for an individual to lay down.

Urinals
There are different types of urinals,But here are the two types based on usage location.
Bowl type urinals – Used in residential buildings.
Stall or Slab type urinals – used in commercial or public buildings.

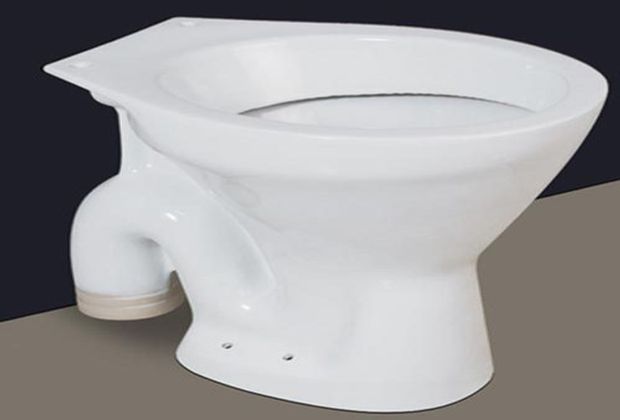
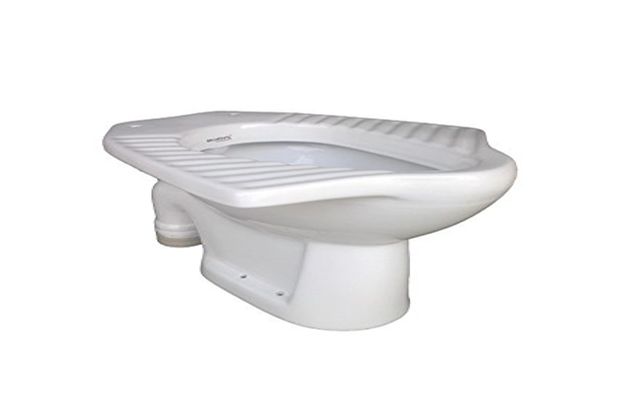
Water Closets
water closets are provided for the purpose of discharging human excreta from the person using it. There are three types of water closets as shown below.



Flush Tanks or Flushing Cistern
Flush tanks are provided along with water closets to discharge water for easy flow of human excreta.
- Valveless siphonic type
- Valve fitted siphonic type
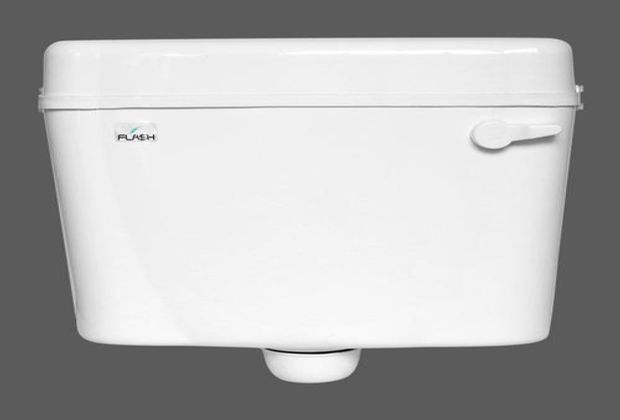
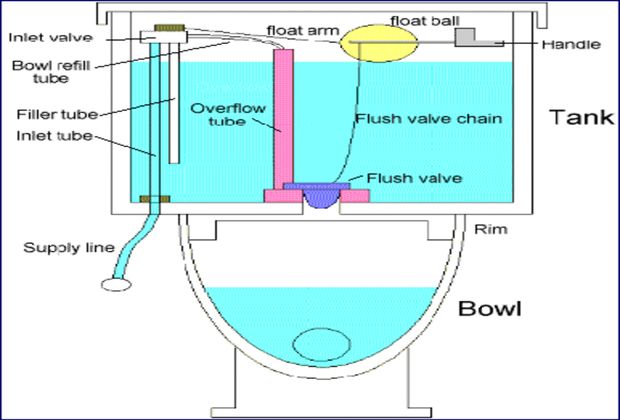

Most commonly used with Indian type is Bell Type Flushing Cistern, is the example of valveless siphonic type flushing cistern.
Also Read – What is sanitary engineering?| Definitions of some common terms

