What is Lintel?
Lintel definition can be stated as, Beam which is placed across the openings like doors, windows etc. in buildings in-order to support or carry the load from the structure above. The width of lintel beam should be equal to the width of wall. Lintel beams ends in the masonry wall to transfer the load carried by them to the masonry walls.
Construction of horizontal lintel beam is easier when compared to arch beams.
The height between floor level above the ground to the window top-level refers to the lintel level. According to building regulations and guidelines, Standard height of lintel for residential building should be 7ft and for commercial buildings it Should be 7.5 ft.
Also read: What is sunken slab?| Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages
Types of Lintel used in Building Construction
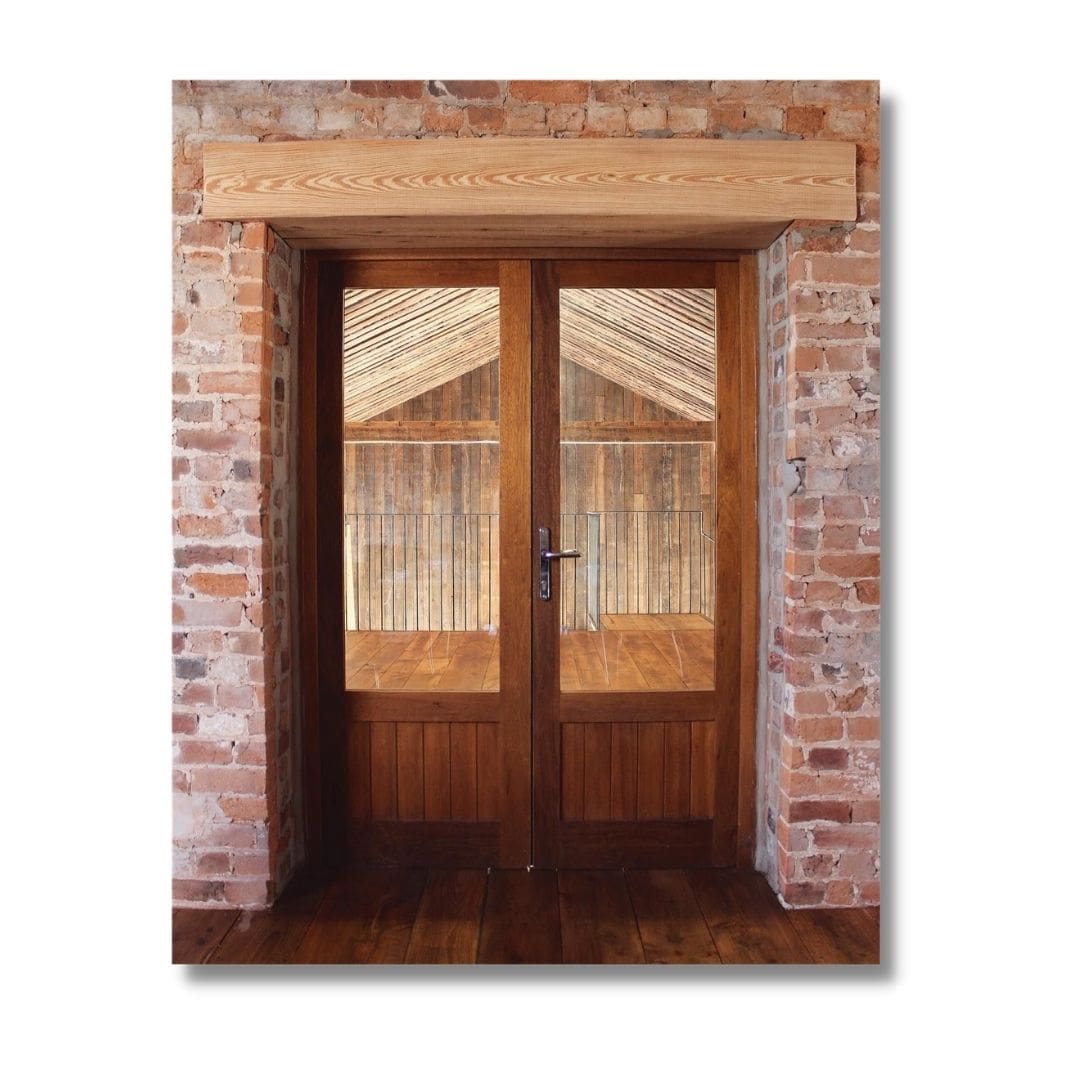
1. Timber Lintel
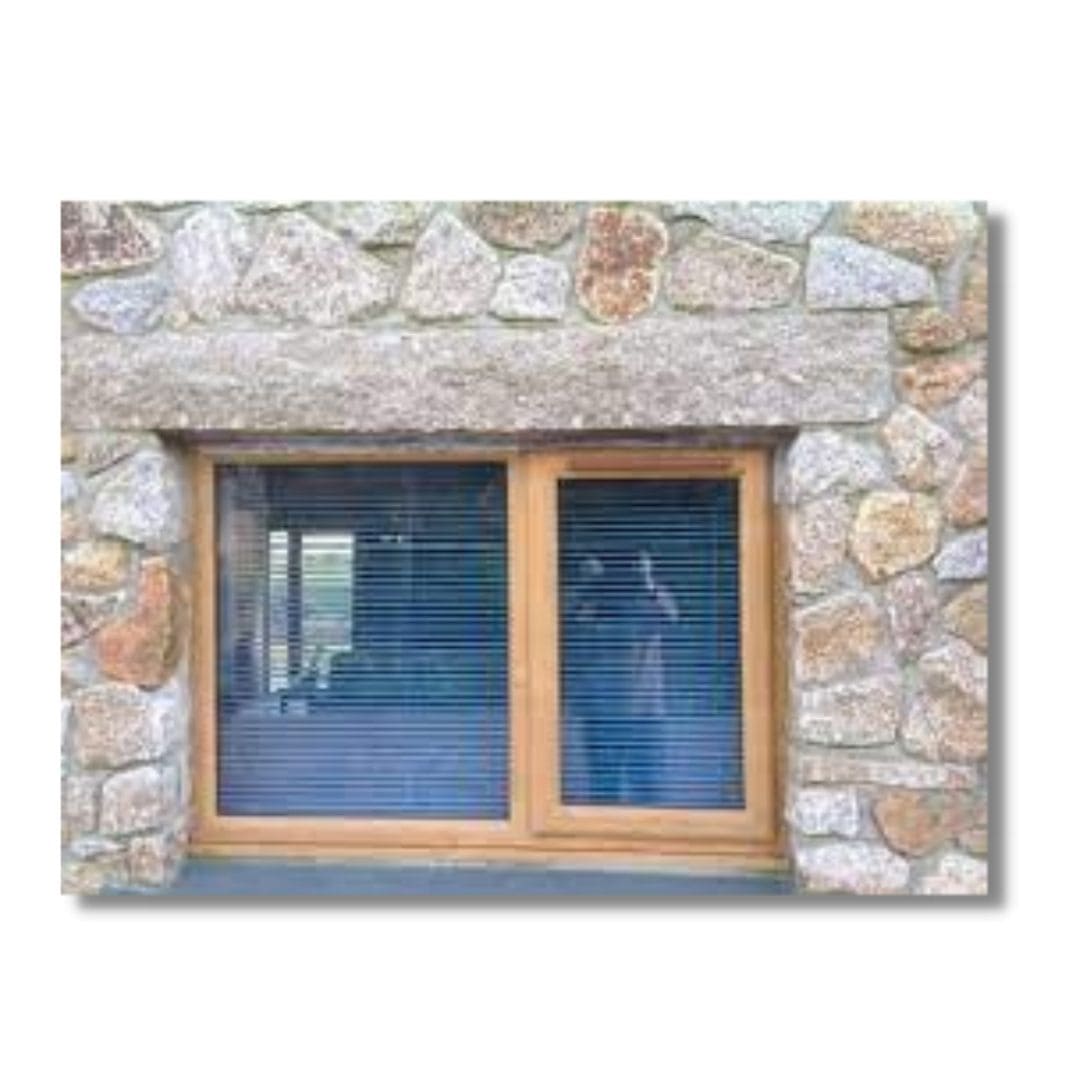
2. Stone Lintel
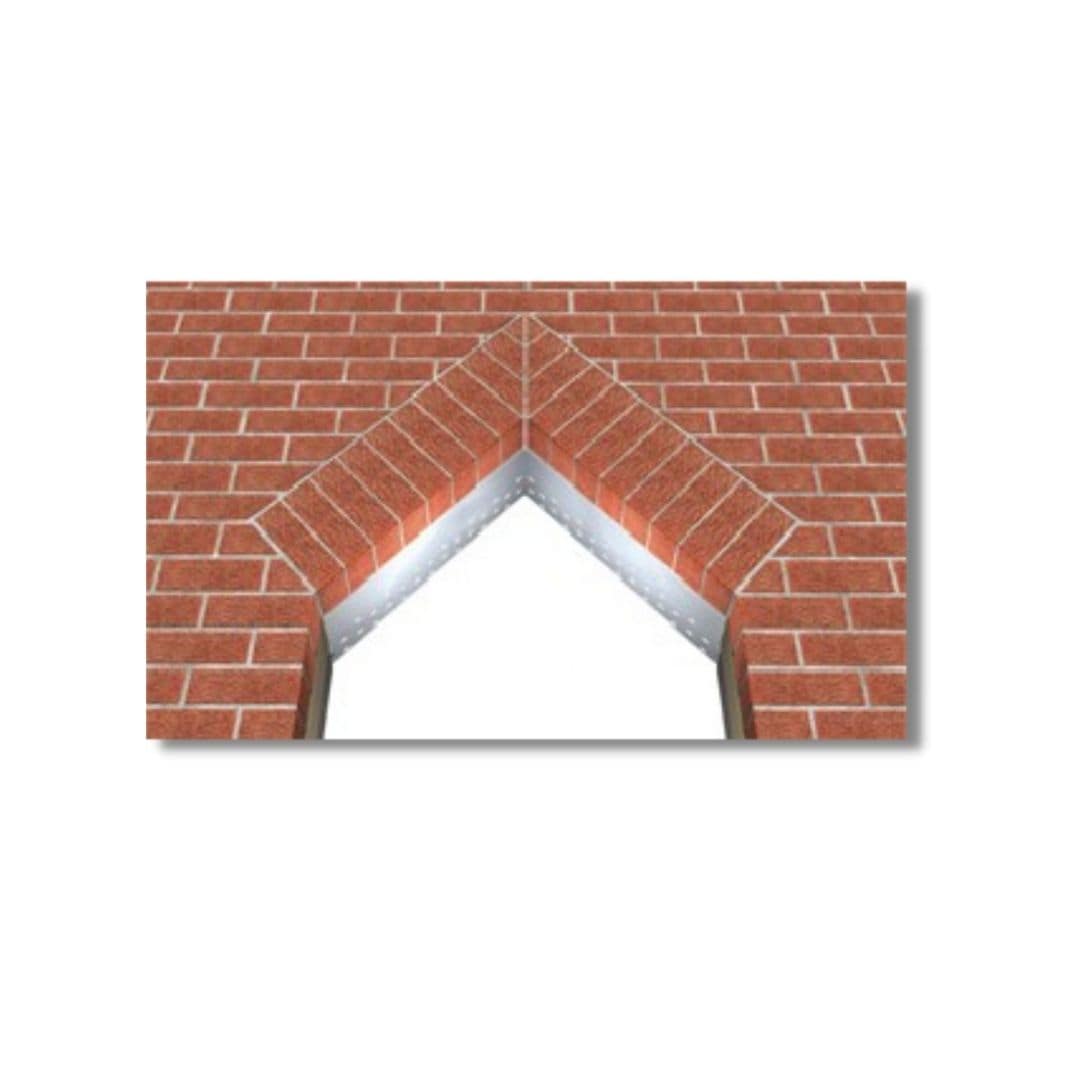
3. Brick Lintel
4. Reinforced brick Lintel
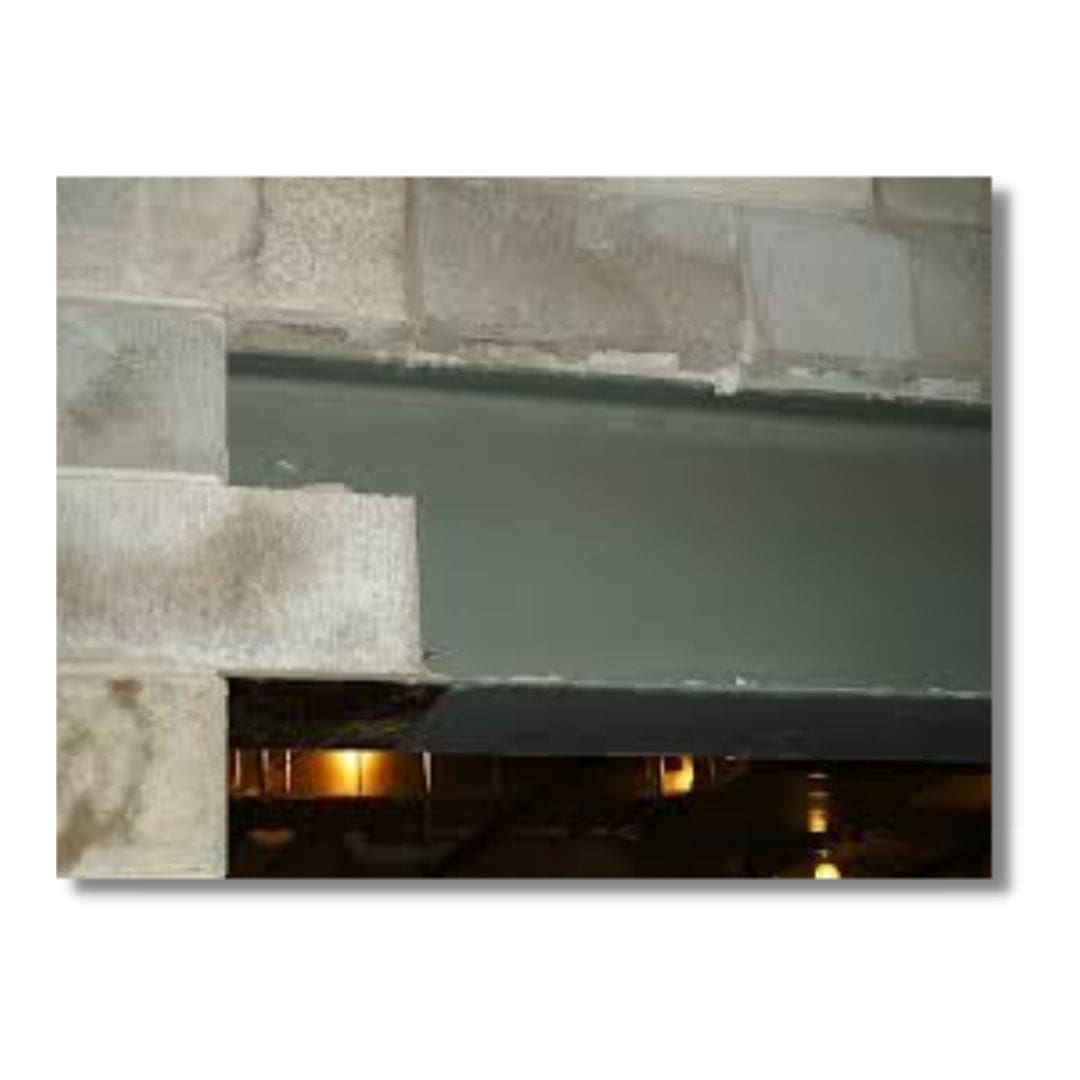
5. Steel Lintel
6. Reinforced concrete Lintel
1. Timber Lintel
These types of lintel beams are generally used during olden days and currently these are replaced by modern methods. Timber lintel are used mainly in hilly regions and these are not cost effective as they cost more and less durable. These are vulnerable to fire.
2. Stone Lintel
Stone lintel are commonly used where there is availability of stones is abundant. The thickness plays major factor in its design.
Stone lintels are also provided over the openings in brick walls. These types of lintel is provided in the form of either one piece or more than one piece.
The depth of stone lintel beam is kept equal to 10 cm / meter of span, with a minimum value of 15 cm. These are used up to spans of 2 meters. In the structure is subjected to vibratory loads, cracks are formed in the stone lintel because of its weak tensile nature. Hence caution is needed.
3. Brick Lintel
Brick lintels are basically used, where the openings are less than 1m and lesser load acting. These type of lintels are built with hard and well burnt first class bricks.
Their depth may varies from 10 cm to 20 cm, depending up on the openings span. Bricks with frogs are more suitable as frogs are filled with mortar gives more shear resistance at the end joints when compared to normal bricks.
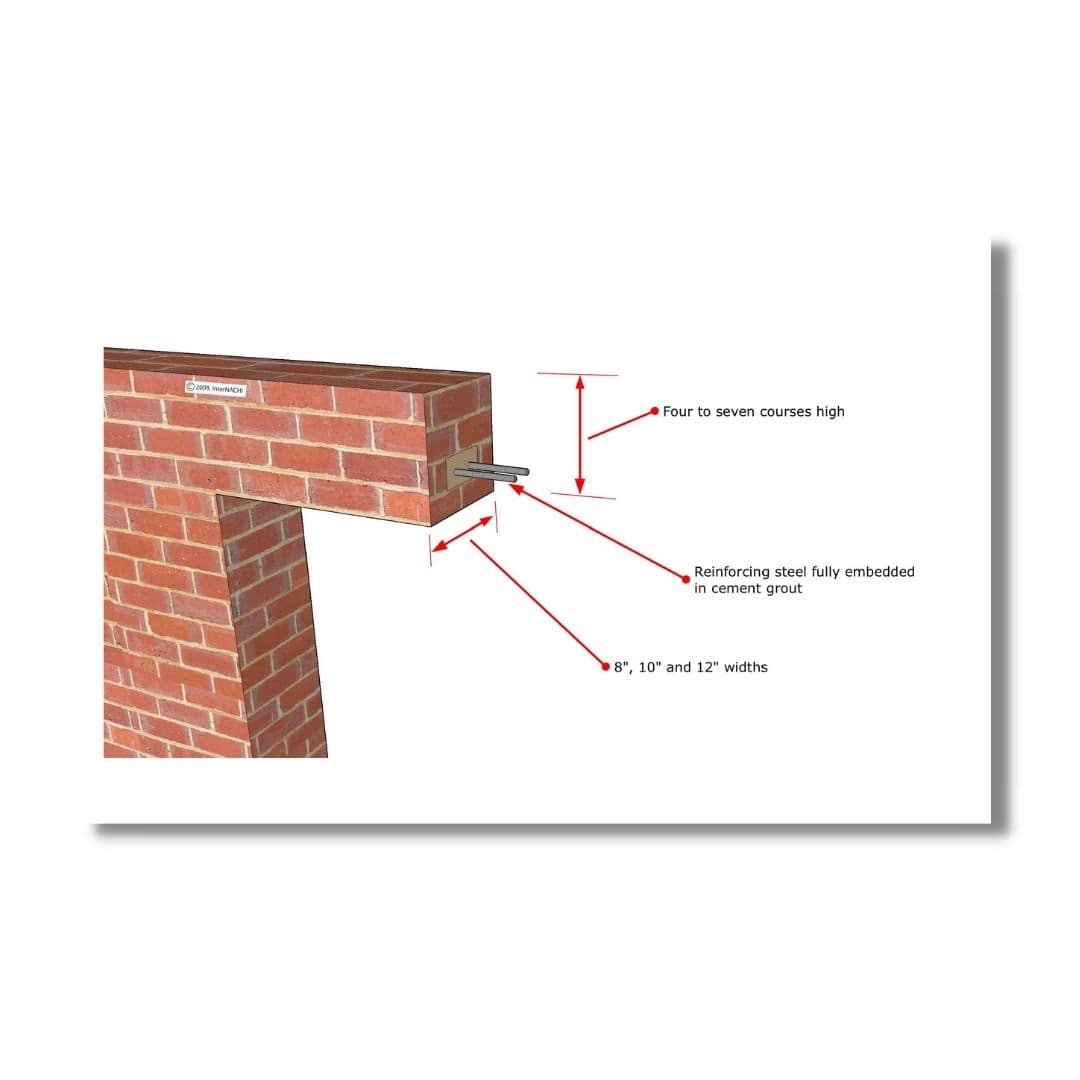
4. Reinforced Brick Lintel
These type of lintel beams are used where loads are heavy and span is greater than 1m. The depth of reinforced brick lintel must be equal to 10 cm or multiple of 10 cm. Arrangement of bricks should be such as there is a 2 to 3 wide space in lengthwise between adjacent bricks for insertion of mild steel bars reinforcement. The gaps are filled with 1:3 cement mortar.
6 mm diameter are provided as Vertical stirrups in every 3rd vertical joint.
8 to 10mm diameter bars are provided at the bottom as Main reinforcement, which are cranked up at the ends.
5. Steel Lintel
These are used when the superimposed loads are heavy and opening gaps are large. Steel lintel beams consist of channel sections or rolled steel joists. Based on the requirement we can use one single section or in combinations of two or more.
Usually, steel joist is either embedded in concrete or cladded with stone facing to keep the width same as width of wall. when two or more units are placed side by side, they are held in position by tube separators.
6. Reinforced Cement Concrete Lintel
Currently, these types of lintel are widely used or adopted to span openings for windows, doors, etc. in building structures. As they are suitable to carry heavy loads and larger spans.
The lintel width should be equal to width of wall and depth of lintel depends on length of span and magnitude of loading. RCC lintels beams can be either precast or cast-in-situ.
Some major advantages to consider such as, they are durable, rigid, strength, fire resistance and economical. And these can be adapted to any shape and size.
Main reinforcement is provided at the bottom to resist tensile stress and half of these bars are cranked at the ends. Shear stirrups are provided to resist shear stress.
Also read-What is fiber reinforced concrete?| Types of Fibers | Properties |Uses